In This Article
Not way back, we seemed to be staring into the abyss of a recession. Goldman Sachs had put the chances of a world recession in 2025 at 60%, though it has now dropped that estimate to 35%. The U.S. Bureau of Financial Evaluation concluded that GDP in Q1 2025 decreased 0.3%, though estimates for Q2 are constructive.
Given this example and the monumental rise in housing costs during the last 15 years, many imagine we’re about to see a repeat of 2008. I defined a while in the past why, even if there may be a recession, there can be no repeat of 2008 within the housing market. However I’ve had sufficient run-ins with offended commenters explaining how the true property market is about to break down to know this angle isn’t universally shared.
A part of it could be that with some darkish financial clouds on the horizon, there’s a tendency to imagine the subsequent financial disaster can be just like the final, regardless of it hardly ever understanding that method, traditionally talking. Nevertheless, a few of it might simply be that sufficient time has handed that many people have forgotten what precisely triggered the biggest actual property meltdown in American historical past.
So, let’s bounce again in time to revisit absolutely the insanity that was the housing market within the first decade of the twenty first century.
“Housing Costs All the time Go Up”
I began investing in actual property in 2005 (good timing, proper?), and one of many first issues I heard was the very odd-sounding phrase, “Housing costs all the time go up.” Admittedly, the phrase itself often got here with a caveat: “OK, not all the time, however nearly.”
Nonetheless, the sentiment hovered about just like the air you breathed on the time and was stated or implied in a thousand alternative ways. Now, clearly, it wasn’t true, however extra importantly, why would anybody even assume this?
A part of the rationale for this mass delusion was that there may be a kernel of fact in it. On a country-wide foundation, housing costs hardly ever go down. Certainly, should you’re on social media, you will have very nicely seen this chart floating round:
Now, keep in mind, this was 2005, so there have been solely two detrimental years between 1950 after which, and each of these have been lower than 1% detrimental. That sounds fairly encouraging, particularly when you examine it to an identical chart for the S&P 500, which is littered with crimson years.
Sadly, whereas the chart is factually right, there are a lot of issues with it. First, it doesn’t return far sufficient. Discover how the Nice Melancholy isn’t included?
This jogs my memory a little bit of Lengthy Time period Capital Administration. The founders gained a Nobel Prize in economics for his or her mathematical method to arbitrage. However that math was solely based mostly on just a few years of knowledge. So when a black swan occasion occurred (particularly, Russia’s debt default in 1998), the corporate collapsed in historic trend. It was so over-leveraged that it threatened to carry down your complete world economic system and ended up requiring a U.S. authorities bailout. (Spoilers for 2008, by the way in which.)
The second drawback with that chart is that it solely appears at nominal returns. Whenever you return to the flip of the century and likewise alter for inflation, the chart appears fairly a bit much less favorable.
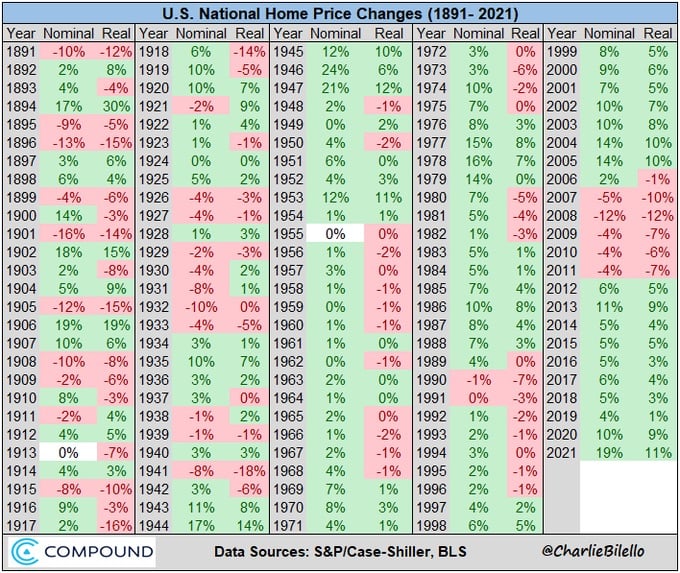
Whenever you put it on a chart, the year-over-year modifications look fairly modest for essentially the most half till simply earlier than the start of the brand new millennium.

(For these questioning why I don’t imagine the latest sharp uptick is close to as problematic as 2008, see right here.)
What actually bought individuals considering that housing costs have been immune to cost corrections was the dot-com bust and the 2001 recession. GDP fell solely 0.6% because of the tech stock-induced bust that triggered the S&P 500 to fall 43% from peak to trough, and the Nasdaq plummeted 75%.
Actual property costs, nonetheless, weren’t simply resilient—they have been nice. Housing costs went up
9.3% in 2000 and 6.7% in 2001 (and over 5% in actual phrases each years). Actual property turned seen as a totally secure haven in distinction to the precarious nature of the inventory market. A kind of irrational exuberance shaped across the housing market.
I keep in mind speaking to at least one vendor in 2006 who stated he needed to carry the property for one more 12 months so he might promote for 10% larger, as if it was some legislation of nature that properties go up in worth on a preset schedule.
The basics underlying the housing market had really fallen fully out of whack and got here right down to Earth with a horrendous thud. From peak to trough, housing costs nationwide fell 30%. The inventory market did even worse, falling virtually 50% and never reaching its pre-crash excessive once more till 2012. Roughly 9 million jobs have been misplaced, and the unemployment fee peaked at over 10%. One estimate discovered that family wealth declined by over $10 trillion.
In 2008, there have been over 2.3 million foreclosures filings, greater than triple the quantity in 2006. And 2009 and 2010 have been each even worse, with over 2.8 million every. The variety of foreclosures filings wouldn’t return to the 2006 stage till 2017.
So Who Did What?
As I’m positive you’ll be able to keep in mind, there was an infinite quantity of debate after the underside fell out about whether or not Wall Road or the federal government triggered the crash. However the factor is, we’d like to embrace the “genius of the AND.”
Wall Road and the federal government each did it. They each did in spades.
We’ll begin by the declare that deregulation triggered the collapse. On this level, the reply is, kind of.
Deregulation myths
The mantra on the left was that greed had triggered the crash, as if greed had simply been invented someday across the flip of the century. When pressed a bit more durable, deregulation could be the acknowledged offender, and that is the place I (partially) diverge from plenty of liberal commentators.
Deregulation did play a job, however oddly sufficient, the most typical scapegoat for deregulation didn’t. That scapegoat was the Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act that was handed in 1999 and overturned a part of the Glass-Steagall Act of 1932.
Glass-Steagall separated industrial banking and funding banking and prohibited any establishment from partaking in each actions. Gramm-Leach-Bliley didn’t even fully undo this half; it simply made it in order that each kinds of companies might be consolidated underneath a single holding firm.
Now, admittedly, I believe there’s an excellent case for separating these two kinds of banks. This laws doubtless contributed to the main consolidation of economic establishments we’ve seen in the previous few many years and helped to embed the “too large to fail” mantra. However there may be little motive to assume this had something to do with the crash. As economist Raymond Natter identified:
“[T]hese allegations by no means specify the precise hyperlink between [Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act] and the disaster. The reason being that there isn’t a readily obvious hyperlink between the 2 occasions. Merely put, the provisions of the Glass-Steagall Act that have been repealed by GLBA didn’t prohibit the origination of subprime mortgage loans, to the securitization of mortgage loans, or to the acquisition of mortgage-backed securities that resulted within the massive losses that banks and different buyers suffered when the housing bubble lastly burst.”
Certainly, should you have a look at the most important banking collapses throughout that disaster, none of them have been performing as or holding each an funding financial institution or industrial financial institution. Lehman Brothers and Bear Stearns have been completely funding banks, and Washington Mutual (the largest financial institution failure in U.S. historical past) was completely a industrial financial institution.
It also needs to be famous that Canada had no equal to Glass-Steagall and but had not a single financial institution failure in 2008. European international locations additionally by no means had any such wall separating industrial and funding banks.
That’s not, nonetheless, to say that regulation (or the shortage thereof) had no half to play.
The function of regulation (and deregulation) within the crash
There are 3 ways wherein I imagine the regulatory framework of the US main as much as 2008 performed a big function within the crash. The primary is the place liberal economists are no less than partially proper. For all of the ink spilled over Gramm-Leach-Bliley, the true piece of deregulation that exacerbated the disaster was the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000. This legislation deregulated over-the-counter by-product trades just like the notorious credit score default swap.
Credit score default swaps started in 1994 earlier than that laws was handed, however they actually took off afterward, particularly as buyers who noticed the crash coming—akin to Michael Burry and John Paulson—purchased them in droves. Credit score default swaps are an absurd monetary instrument the place a monetary establishment pays a third-party investor a stream of month-to-month funds until an underlying mortgage goes into default, wherein case the establishment pays out the safety’s worth to the investor.
Credit score default swaps successfully act as a kind of bizarro-world insurance coverage the place the insurance coverage firm pays month-to-month premiums to you until your own home burns down, wherein case, it’s a must to pay the insurance coverage firm the fee to restore your house.
This elevated the demand for mortgage-backed securities, but it surely definitely didn’t in and of itself trigger the housing disaster, nor even the housing bubble to inflate as a lot because it did. However what it completely did do was dramatically exacerbate the monetary carnage as soon as the bubble began to deflate, as monetary establishments needed to cope with each large losses on their loans and plenty of additionally needed to pay out enormous lump sums on all of the credit score default swaps that they had bought.
AIG—which specialised in promoting insurance coverage to monetary establishments and ended up requiring the largest authorities bailout—was particularly hammered by its publicity to credit score default swaps.
The second drawback with the regulatory framework was what economists seek advice from as ethical hazard. This refers back to the expectation massive monetary companies have that if issues actually go sideways, Uncle Sam will foot the invoice. This expectation creates an incentive to interact in dangerous habits. In any case, should you went to Vegas and knew the federal government would choose up the tab should you misplaced, wouldn’t you simply let it journey?
You may also like
It’s principally forgotten right now, however the Nineteen Nineties noticed a wave of presidency bailouts. First, in 1989, the U.S. authorities supplied $50 billion to bail out failed Financial savings and Loans establishments. In 1995, the federal government supplied a $50 billion bailout to Mexico to assist stabilize the peso. In 1998, the federal government organized the aforementioned $3.6 billion bailout of Lengthy Time period Capital Administration simply after it was providing bailouts to South Korea and Indonesia in the course of the 1997 Asian Monetary Disaster.
It had simply grow to be frequent knowledge that in case your financial institution was large enough and also you ran it into the bottom, the taxpayers would choose up the tab (and you can nonetheless give your self a pleasant bonus afterward for such day’s work).
Evidently, such incentives didn’t assist. However it bought even worse when the disaster really got here, and the federal government acted erratically by bailing out Bear Stearns whereas letting Lehman Brothers fail. This left buyers at the hours of darkness as to what to anticipate.
Lastly, the federal government did not enact any regulation that might need stopped or no less than blunted the affect of the housing bubble. Brooksley Born, as chair of the Commodity Futures Buying and selling Fee, tried to manage derivatives, however with out any luck.
Past that, the federal government made no try to deflate what was changing into a transparent bubble. The ratio of median annual revenue to housing costs had grown from 3.5 in 1984 to five.1 in 2007. By itself, this would possibly not have raised an alarm, as rates of interest have been a lot decrease in 2007 than they have been in 1984. However just a bit digging made it simple to see simply how fragile the market really was.
For one, virtually 35% of mortgages being taken out on the eve of the crash have been adjustable-rate loans, usually with low-interest “teaser” charges.
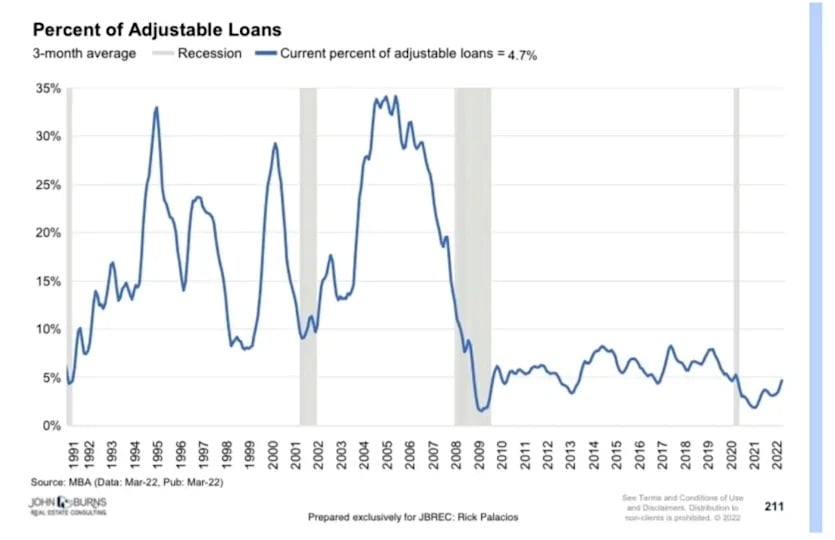
Moreover, the variety of poorly certified patrons ought to have been extraordinarily disconcerting. Whereas about 75% of mortgages originated in 2022 had a credit score rating of 760 or extra, that was lower than 25% in 2007. Round 15% had credit score scores underneath 620.

At no level did the federal government make a concerted effort to rein in adjustable-rate, teaser loans, acknowledged revenue approvals (the dreaded NINJA loans: No Revenue No Job No Property), or something like that. Actually, they have been too busy pouring gasoline on the fireplace.
The federal government’s function within the disaster
The federal government’s function as watchdog for the monetary markets was extra a case of the fox guarding the hen home. As an alternative of deflating the housing bubble, the federal government’s actions have been clearly geared towards blowing it up.
In a case of bipartisan madness, the Democrats’ push for reasonably priced housing and the Bush administration’s push for an “possession society” coalesced right into a ticking time bomb. Apparently, proudly owning a house was all that mattered. Whether or not you can afford it was a query solely Debbie Downers preferred to ask.
A wide range of legislative acts have been handed to extend homeownership and encourage banks to lend to low-income households. Probably the most well-known of those acts was the 1977 Neighborhood Reinvestment Act, which the Clinton administration used way more aggressively than earlier administrations had.
But this was solely a small piece of the puzzle. The large issues concerned the Federal Reserve and the 2 most well-known government-sponsored entities, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. We’ll begin with Fannie and Freddie.
In 1999, Steven Holmes wrote an notorious piece for The New York Instances, “Fannie Mae Eases Credit score to Help Mortgage Lending.” In it, he wrote, “[T]he Fannie Mae Company is easing the credit score necessities on loans that it’ll buy from banks and different lenders.”
Holmes went on to cite then-Fannie Mae CEO Franklin Raines:
“Fannie Mae has expanded homeownership for tens of millions of households within the Nineteen Nineties by lowering down cost necessities. But there stay too many debtors whose credit score is only a notch beneath what our underwriting has required who’ve been relegated to paying considerably larger mortgage charges within the so-called subprime market.”
Holmes then ominously notes, “In shifting, even tentatively, into this new space of lending, Fannie Mae is taking up considerably extra threat.”
You assume?
Fannie Mae was arrange within the wake of the Nice Melancholy to purchase mortgages on the secondary market in an effort to increase homeownership. Freddie Mac was later created in 1970 to increase the secondary market with an added give attention to serving smaller monetary establishments. Mixed, they assist a whopping 70% of the mortgage market in the US.
Fannie and Freddie led the cost on increasing mortgage-backed securities, with over $2 trillion in MBS in 2003 and dwarfing all personal establishments till 2005. Roughly 40% of all newly issued subprime securities have been bought by both Fannie or Freddie within the run-up to the monetary disaster. And these establishments typically set the tone for different market members to comply with.
Keep in mind, that New York Times article got here out in 1999. Right here’s what occurred to subprime within the years that adopted.

Subprime adjustable-rate mortgages ended up having an astronomical delinquency fee—over 40%! Alternatively, prime fixed-rate mortgages by no means had a delinquency fee exceeding 5%, even on the peak of the disaster.
The Federal Reserve additionally had a main function to play. The truth that the then-Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke might declare “the troubles within the subprime sector on the broader housing market can be restricted, and we don’t count on vital spillovers” in Might 2007 reveals, at greatest, they have been asleep on the wheel. However the Fed’s function within the disaster is far deeper than that.
It goes again to the 2001 dot-com bust. It was at the moment that economist Paul Krugman gave his notorious recommendation on the best way to get the economic system again on its ft:
“To struggle this recession, the Fed wants greater than a snapback; it wants hovering family spending to offset moribund enterprise funding. And to do this, as Paul McCulley of Pimco put it, Alan Greenspan must create a housing bubble to interchange the Nasdaq bubble.”
And that’s precisely what the Fed did.
Regardless of the 2001 recession being fairly delicate, the Fed held rates of interest at (what have been then) historic lows. The Fed pushed the federal funds fee down from about 6.5% in 2001 to 1%, after which held it there till the center of 2004.
Austrian economists like to speak about the “pure fee of curiosity,” particularly, what rates of interest could be in the event that they have been set by the market, given the demand for loans and the quantity of financial savings out there. Keynesian economists would argue that it’s not so easy. No matter that controversy, there may be definitely a pure vary of curiosity. And given the robust rebound from the 2001 recession (i.e., excessive demand) and abysmal financial savings fee on the time (i.e., low provide), the value of cash ought to have been considerably larger than it was.
(On a facet word, when loans go into default, cash is actually taken out of existence, which is a main motive that, regardless of very low rates of interest after the disaster, inflation was low and, no less than for some time, asset costs didn’t skyrocket.)
At the start of this text, I famous how actual property costs elevated by over 5% in actual phrases in 2001. This is why. The Fed’s excessively low charges inflated housing costs, making a false sense that actual property all the time went up.
And given each the federal government’s habits and Wall Road’s habits, that extra liquidity made its method into blowing up the true property bubble (each earlier than and after the bubble burst in numerous methods).
Wall Road’s function within the disaster
I’m typically in favor of a free market, however I do discover it a bit odd the way in which many defenders of capitalism blamed all of it on the federal government within the wake of the 2008 monetary disaster. It was as if poor Goldman Sachs and the downtrodden Countrywide simply needed to make a bunch of farcically advanced derivatives as a result of the federal government was pushing banks to lend extra and extra to much less and less-qualified debtors.
We should always keep in mind that 60% of subprime mortgages didn’t go to Fannie and Freddie. These have been issued by industrial banks themselves. After which these horrible loans have been securitized into obscure monetary devices that hid their underlying threat and offered everywhere in the world, as can be mentioned shortly.
No, Wall Road’s habits earlier than the crash was atrocious. Though it wasn’t simply Wall Road, sadly. The issues have been systemic.
For one, there was a disastrous disconnect between these issuing loans and people shopping for them. Mortgage originators bought paid for issuing loans. As soon as they have been issued, the issuer would promote the mortgage and transfer on to the subsequent borrower. The incentives have been all backwards.
And as one would possibly count on, such horrible incentives laid the groundwork for rampant fraud. A paper by John M. Griffin on the function of fraud within the disaster is price quoting at size:
“Underwriting banks facilitated wide-scale mortgage fraud by knowingly misreporting key mortgage traits underlying mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Beneath the cowl of complexity, credit standing companies catered to funding banks by issuing more and more inflated scores on each RMBS and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). Originators who engaged in mortgage fraud gained market share, as did CDO managers who catered to underwriters by accepting the lowest-quality MBS collateral. Appraisal focusing on and inflated value determinations have been the norm.”
The collateralized debt obligations talked about by Griffin have been packages of mortgages that Wall Road companies usually sliced and diced in a method to obscure the underlying threat. These devices supplied the phantasm of diversification. However on condition that, no less than for the decrease tranches of such CDOs, that diversification amounted to nothing greater than a various array of rubbish, it didn’t supply a lot safety.
In the long run, as Niall Ferguson concluded, “The sellers of structured merchandise boasted that securitisation allotted belongings to these greatest capable of bear it, but it surely turned out to be to these least capable of perceive it.”
The disaster was globalized by this fashion of securitizing rubbish and promoting it off to the unsuspecting. (Though, whereas the worldwide disaster began in the US, many different international locations had housing bubbles as nicely.)
Lastly, there have been the ranking companies that constantly put their triple-A stamp of approval on farcically advanced securities, backed by subprime, teaser-rate NINJA mortgages proper up till the entire home of playing cards collapsed. The largest drawback with these companies was fairly easy: They’re “issuer-paid,” which created an infinite battle of curiosity.
The right function of economic establishments is to successfully distribute capital in a way that enables entrepreneurs to increase their companies and customers to buy houses and different costly belongings they’ll afford, and to take action in a method that grows the economic system whereas mitigating threat. What really occurred, nonetheless, was that all through the run-up to the collapse, Wall Road did nearly nothing to ameliorate threat, and as a substitute engaged in extraordinarily dangerous, extremely leveraged, and overly advanced habits to maximise earnings in essentially the most myopic and shortsighted method attainable. The outcomes shouldn’t have been shocking.
They definitely deserved no pity, nor our tax {dollars} (though that’s one other story).
Last Ideas
The 2008 monetary disaster was simply the largest financial catastrophe of my lifetime and has had lasting results on the true property trade, in addition to the economic system as a complete. Certainly, it’s had an infinite impact on our collective psyche, significantly for these of us in actual property. In a variation of Godwin’s Legislation, the longer a dialog about actual property goes, the probability of the 2008 actual property crash being introduced up approaches one.
Currently, many have been warning that we face a second such crash. Once more, that’s extremely unlikely. The basics of actual property are far sounder now than then. Monetary crises and recessions hardly ever play out the identical method twice in a row.
In 1929, it was an overvalued inventory market and a foolhardy try to return to the gold customary at pre-World Warfare I costs. Within the ‘70s, it was an oil shock and the inflationary penalties of “weapons and butter”; in 2001, it was the dot-com bust; in 2008, it was housing; and allow us to not neglect, in 2020, a pandemic.
Subsequent time round, given the method issues are going, it very nicely would possibly be a sovereign debt disaster. Hopefully not. However both method, it’s nonetheless essential to grasp how such a catastrophe took place to keep away from it from taking place once more, and likewise in order to not assume a run-up in costs essentially means it’s taking place once more.
Analyze Offers in Seconds
No extra spreadsheets. BiggerDeals reveals you nationwide listings with built-in money circulate, cap fee, and return metrics—so you’ll be able to spot offers that pencil out in seconds.




















