That is Bare Capitalism fundraising week. 532 donors have already invested in our efforts to fight corruption and predatory conduct, notably within the monetary realm. Please be a part of us and take part through our donation web page, which exhibits the right way to give through examine, bank card, debit card, PayPal, Clover, or Clever. Examine why we’re doing this fundraiser, what we’ve completed within the final yr, and our present objective, supporting the commentariat.
For the primary time in additional than 50 years, the world’s two largest nuclear powers function and not using a single binding restrict on the dimensions of their arsenals. The Strategic Arms Discount Treaty (START I) and its successor frameworks, START II and New START, have been the spine of U.S.–Russian nuclear restraint, inserting ceilings on deployed warheads and creating essentially the most strong verification system in arms-control historical past. Because the clock runs out on New START’s closing extension in February 2026, the construction that anchored world strategic stability is dissolving. Its disappearance marks not solely the lapse of a treaty, however the erosion of a philosophy: that nuclear powers can handle arms competitors by means of transparency, predictability, and regulation. This text describes the background and traits of the START treaties and the possible penalties of abandoning them.
MIRV nuclear warheads – The less the higher
Origins and Evolution of START
START emerged from the late Chilly Struggle recognition that an unconstrained arms race was each unaffordable and threatening. START I, signed in 1991 and getting into into pressure in 1994, required both sides to chop deployed strategic warheads to six,000—a dramatic discount from Chilly Struggle peaks—and launched on-site inspections, telemetry sharing, and detailed knowledge exchanges. A follow-on, START II (1993), sought deeper cuts and a ban on multiple-warhead land-based missiles (MIRVs) however by no means took impact after Russia withdrew in protest of the U.S. exit from the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The spirit of restraint revived in 2010 with New START, limiting both sides to 1,550 deployed warheads on 700 launchers and modernizing verification procedures. Prolonged as soon as by mutual consent in 2021, New START now stands because the final surviving U.S.–Russian arms-control accord—and it’s expiring with no alternative in sight.
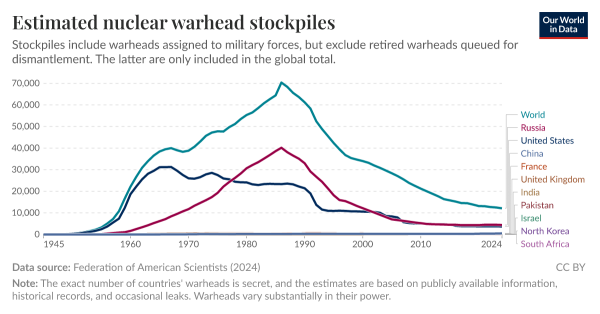
Why START Mattered
Main discount in warheads. Beneath the START treaties, the variety of nuclear warheads worldwide declined considerably from over 50,000 to round 10,000.
Predictability. By mandating common knowledge exchanges, START changed hypothesis with details. All sides knew the opposite’s arsenal dimension and composition, eradicating incentives to plan in opposition to inflated threats.
Verification. The treaty’s inspection regime, together with over 18,000 on-site visits since 1994, grew to become the gold commonplace for confidence constructing. Inspectors verified missile serial numbers, launch-tube counts, and base inventories, confirming declared reductions.
Disaster Stability. Quantitative ceilings narrowed the advantages of a primary strike and fostered a secure deterrence steadiness. Leaders might calculate, not speculate, in moments of rigidity.
Symbolic Energy. START proved that adversaries might negotiate in good religion. Its success lent credibility to the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and impressed parallel efforts such because the Intermediate-Vary Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty. Arms management was not charity; it was strategic insurance coverage.
The Rise and Fall of Nuclear Arms Management
The Cuban missile disaster led to a willingness to have interaction in arms management diplomacy between the U.S. and the us. Starting with the Nuclear Check Ban Treaty in 1963, a sequence of treaties succeeded in decreasing tensions among the many nuclear powers and inhibiting arms racing. Only some of those treaties are nonetheless in pressure.
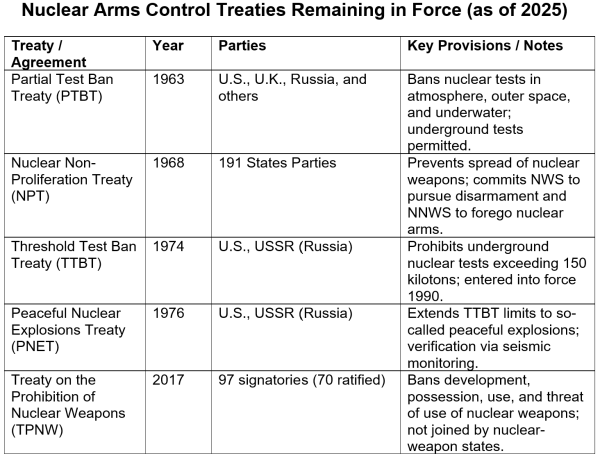
Starting in 2002, rising tensions between the U.S. and Russia led to the abrogation or lapsing of an important nuclear arms management treaties. Perverse incentives of political expediency and army aggrandizement resulted within the elimination of those vital safeguards in opposition to nuclear conflict and moved the doomsday clock nearer to midnight. New START, the final of the nuclear arms discount treaties, will lapse in February of 2026.
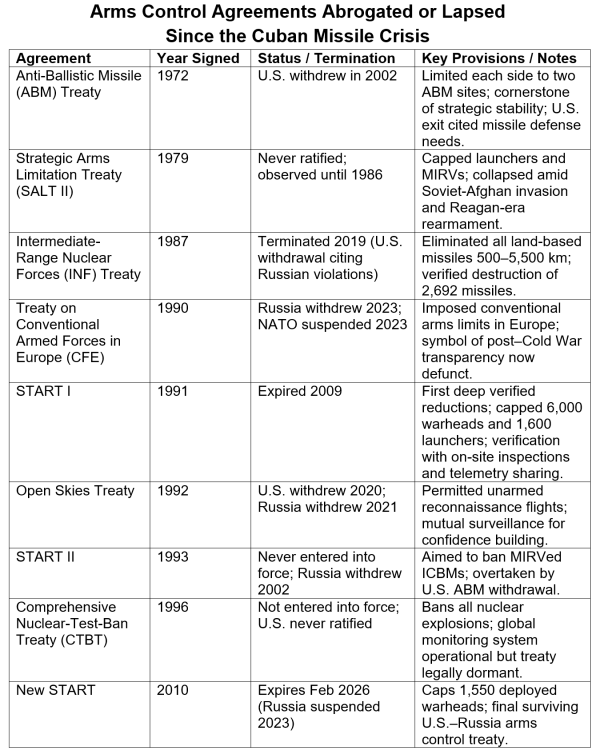
The unraveling of the START treaties started with deteriorating belief after 2014, when Russia’s annexation of Crimea and subsequent sanctions froze broader dialogue. COVID-19 halted on-site inspections in 2020 and so they by no means totally resumed. In February 2023, Moscow suspended participation in New START, citing Washington’s “hostile actions” and NATO enlargement. The USA accused Russia of noncompliance for refusing inspections and knowledge updates. With conflict raging in Ukraine and bilateral diplomacy at its lowest ebb for the reason that early Nineteen Eighties, neither capital is getting ready a successor treaty. Because the 2026 deadline approaches, START is technically alive however functionally defunct. Putin just lately proposed a one-year extension of New START, however there was no reply from the Trump administration.
Penalties of New START Expiration
Return of the Arms Race. With out ceilings, each powers are free to increase their arsenals of deliverable warheads. The USA is modernizing each leg of its triad: the Sentinel ICBM, B-21 bomber, and Columbia-class submarines. Russia is fielding new techniques such because the Sarmat heavy missile and Avangard hypersonic glide automobile. Missing mutual limits, planners will assume worst-case development, inviting a expensive and destabilizing buildup harking back to the Nineteen Sixties. Each the U.S. and Russia might carry their MIRV missiles as much as full deliverable warhead capability by including warheads from current inventories.
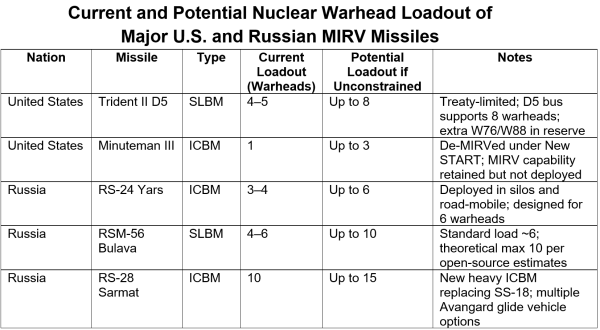
Collapse of Verification. As soon as inspections finish, intelligence estimates should fill the hole. Satellite tv for pc imagery can rely silos however not warheads; telemetry could be spoofed. The disappearance of verified knowledge will pressure both sides to hedge with extra capability, compounding distrust.
Disaster Instability. In a confrontation between nuclear powers, leaders will function with better threat. Uncertainty about pressure survivability could push either side towards launch-on-warning postures, shrinking determination time and elevating the percentages of miscalculation.
World Ripple Results. Nice-power restraint has underpinned the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) discount: non-nuclear states resign weapons in change for nuclear powers’ dedication to disarmament. If Washington and Moscow abandon limits, Beijing, New Delhi, Islamabad, and Pyongyang achieve precedent to increase unchecked. Allies underneath the U.S. umbrella could query prolonged deterrence, spurring requires impartial capabilities.
Breakdown of Nuclear Diplomacy. Since SALT I (1972), a number of treaties have affirmed that nuclear extra is harmful and reversible. Their collective erosion, with INF useless, Open Skies withdrawn, now START expiring, indicators a brand new period of diplomatic nihilism, the place energy alone dictates numbers.
China’s Nuclear Deterrent and a Three-Physique Downside
Maybe the worst consequence of the abandonment of START could be the elevated incentive for China to construct up its nuclear forces. Traditionally, China maintained a “minimal deterrent” (~400–500 warheads, rising towards 1000 by early 2030s, per U.S. DoD estimates). Its doctrine depends on assured retaliation. START’s dissolution would alter this assumption.
If the U.S. and Russia increase past 1,550 deployed warheads, the hole between Chinese language and different superpower arsenals widens dramatically. Credibility of China’s second-strike deterrent diminishes as a result of U.S. and Russian counterforce capabilities would outpace China’s survivable forces. Not solely would China face a rising U.S. nuclear arsenal, it must defend in opposition to the opportunity of a mixed strike by the U.S. and Russia. The chance that every social gathering in a nuclear deterrence triad would possibly confront a joint assault by the opposite two creates an unstable “three-body downside” as a result of every social gathering’s effort to match the mixed arsenal of the opposite two creates an asymmetry with every of the opposite two, which drives a self-perpetuating cycle of arsenal development.

China’s DF-61 ICBM – Huge hassle for arms management
Prospects for Renewal or Substitute
Reviving formal arms management faces formidable political headwinds. In Washington, Congress stays cautious of treaties amid partisan divides. Moscow, underneath sanctions and wartime censorship, views strategic arms negotiations as a concession. Nonetheless, slender confidence-building measures are conceivable: restricted data-transparency accords, mutual check notifications, and moratoria on new deployment classes (e.g., space-based weapons). Long term, stability would require tripartite engagement with China, whose arsenal complicates bilateral ceilings. But Beijing rejects verification parity till its forces close to U.S.–Russian ranges. Within the absence of a grand treaty, policymakers could accept casual norms and reciprocal statements, a fragile substitute for legally binding limits.
Conclusion
START’s expiration is greater than one other lapsed treaty; it’s the elimination of the final barrier separating structured deterrence from unconstrained rivalry. With out the START verification mechanism, conservative assumptions will rule and a nuclear arms race will resume, resulting in rising protection budgets, hair-trigger alerts, and crises threatening disaster. Restoring arms management treaties, even at a modest stage, is an pressing precedence. Transparency is cheaper than rearmament, and treaties, nonetheless imperfect, are extra dependable than notional deterrence. It’s critically vital for the protection of mankind that the New START treaty be renewed, and that additional arms management agreements be carried out. It took many years to construct nuclear belief. Letting START lapse might usher in a deadly new period of nuclear terror.





















