New information from the Bureau of Financial Evaluation verify that inflation remained low in Could. The Private Consumption Expenditures Worth Index (PCEPI), which is the Federal Reserve’s most popular measure of inflation, grew at an annualized price of 1.6 % final month. It has averaged 1.1 % during the last three months and a couple of.3 % during the last yr.
Core inflation, which excludes risky meals and vitality costs but in addition locations extra weight on housing providers costs, was a bit increased. In accordance with the BEA, core PCEPI grew 2.2 % in Could. It has averaged 1.7 % during the last three months and a couple of.7 % during the last yr.
Inflation is working properly under the latest projections submitted by Fed officers. In June, the median Federal Open Market Committee member projected 3.0 % PCEPI inflation for 2025, with projections starting from 2.5 to three.3 %. PCEPI inflation has averaged simply 2.6 % year-to-date, which is above the projections submitted by eighteen of 19 FOMC members.
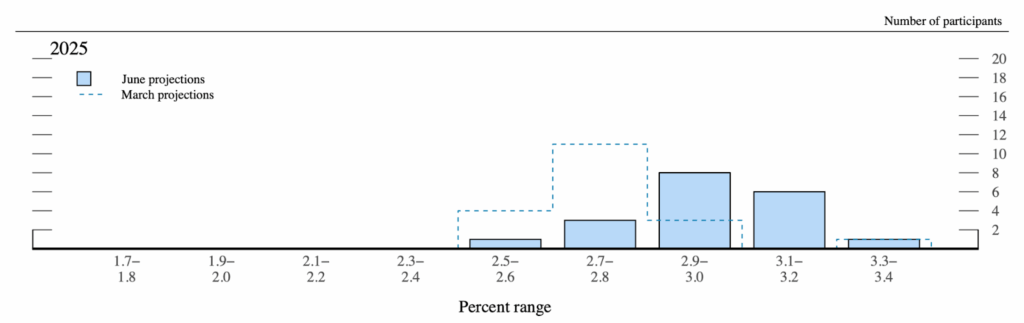
Actually, inflation has been working a lot nearer to the projections Fed officers submitted again in March. Three months in the past, the median FOMC member projected 2.7 % inflation for 2025. At the moment, projections ranged from 2.5 to three.4 %, however the central tendency (i.e., excluding the three highest and three lowest projections) was 2.6 to 2.9 %. In March, just one member projected inflation would exceed 3.0 % this yr. In June, seven members projected inflation above 3.0 %.
What modified? Quickly after submitting their projections in March, Fed officers realized how excessive and widespread President Trump’s supposed tariff charges could be. Ongoing negotiations, court docket orders, and Congressional push again now recommend these tariff charges will probably be decrease — and, in some circumstances, a lot decrease — than these introduced in April. Nonetheless, the tariff charges seem to stay increased than Fed officers anticipated they might be again in March.
Broadly talking, there are two methods the inflation information may evolve within the months forward. Within the first situation, the pass-through from tariffs will trigger costs to rise significantly over the again half of this yr. Given year-to-date information, inflation must common 3.3 % over the rest of 2025 to hit the median FOMC member’s projection. That’s greater than double the inflation price realized in Could, and seventy foundation factors above the common inflation price realized during the last yr. Within the second situation, the place passthrough from tariffs is way decrease than most Fed officers anticipate, inflation will proceed falling, stay regular, or rise barely.
In idea, the passthrough from tariffs to the value stage shouldn’t have any impact on financial coverage. The tariffs are a unfavourable provide shock, which the Fed is unable to mitigate. One of the best the Fed can do (with or with out the unfavourable provide shock) is stabilize demand — that’s, to maintain nominal spending on a steady trajectory.
The latest projections seem per this look-through-supply-shocks method. Whereas the median projection for inflation rose significantly from March to June, the implied median projection for nominal spending — which might be constructed by including the median projections for inflation and actual GDP progress — remained unchanged at 4.4 %.
Financial coverage is extra sophisticated in observe, nevertheless. The general public won’t react to the passthrough from tariffs the best way the rational brokers in an financial mannequin do. Particularly, the general public may mistake the short-term enhance in inflation attributable to an antagonistic provide shock as a everlasting enhance in inflation, and revise their inflation expectations accordingly. Fed officers would then want to fulfill these increased expectations with sooner nominal spending progress, thereby delivering the completely increased inflation anticipated; or, go away nominal spending progress unchanged and threat a recession.
On the post-meeting press convention final week, Fed Chair Jerome Powell acknowledged the chance that tariffs will push inflation expectations increased:
The consequences on inflation could possibly be short-lived, reflecting a one-time shift within the worth stage. It’s additionally doable that the inflationary results may as a substitute be extra persistent. Avoiding that end result will rely upon the dimensions of the tariff results, on how lengthy it takes for them to go by means of absolutely into costs, and finally on conserving long term inflation expectations properly anchored. Our obligation is to maintain long term inflation expectations properly anchored and to forestall a one-time enhance within the worth stage from turning into an ongoing inflation drawback.
In different phrases, the Fed may have to hold coverage tighter than could be preferrred with a view to reassure the general public that the supply-driven inflation will probably be short-term.
If financial coverage have been near impartial at present, holding the federal funds price goal barely above impartial with a view to hold inflation expectations well-anchored would have little unfavourable impact on near-term financial exercise and a impartial to optimistic impact on long term financial exercise. If financial coverage is already excessively tight, nevertheless, the Fed’s hesitancy to chop the federal funds price goal in response to lower-than-expected nominal spending progress may considerably scale back financial exercise within the close to time period, exacerbating the actual results of upper tariffs. Simply because the Fed’s hesitancy to boost charges in 2021 and early 2022 allowed inflation to rise, its hesitancy to chop charges within the months forward would threat inflicting a recession.




















